Chronic respiratory diseases can be perplexing and challenging to manage, especially when it comes to differentiating between conditions that share some similarities but have distinct causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches. Two such conditions are bronchiectasis and emphysema. Although both are lung disorders that affect breathing, they have different underlying mechanisms, risk factors, and management strategies. This article will explore the key differences between bronchiectasis and emphysema, helping you understand these conditions more clearly.
Contents
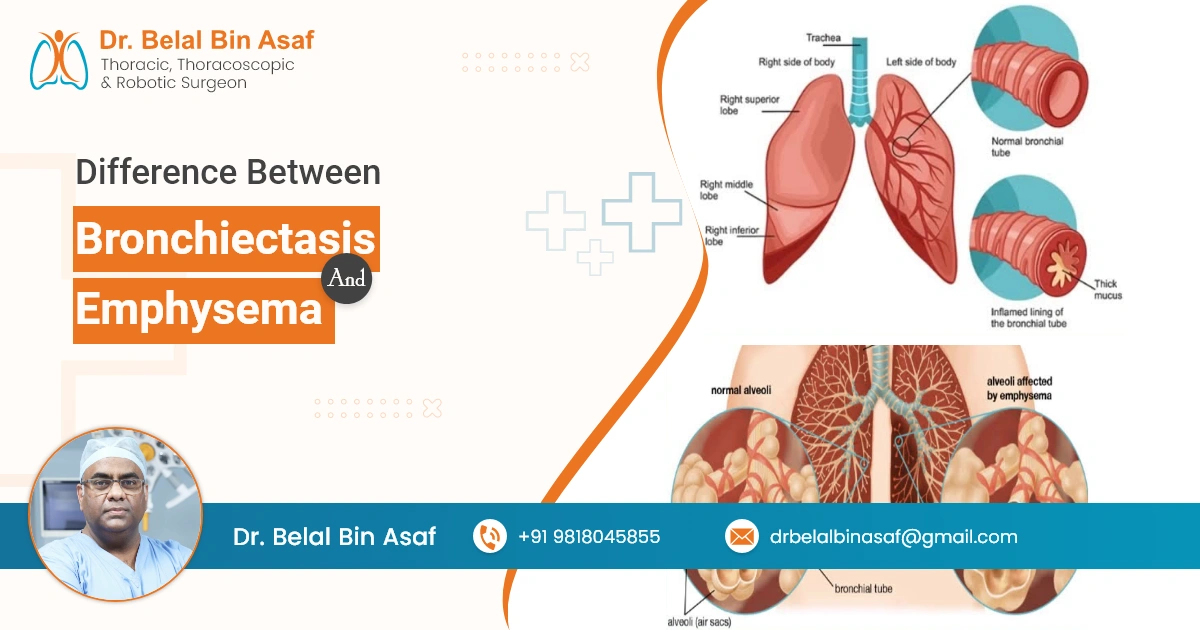
What is Bronchiectasis?
Bronchiectasis is a chronic condition characterized by the abnormal widening and scarring of the airways, leading to impaired airflow and difficulties in clearing mucus from the lungs. The damaged airways become flabby and dilated, making it easier for bacteria and mucus to accumulate, which in turn leads to chronic infections, inflammation, and further lung damage.
Causes of Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis can result from various factors, including:
- Infections: Chronic respiratory infections such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, or whooping cough can lead to permanent airway damage.
- Genetic conditions: Conditions like cystic fibrosis, which leads to thick, sticky mucus in the lungs, are a major cause of bronchiectasis.
- Immune system deficiencies: Certain immune system disorders, like common variable immunodeficiency, may impair the body’s ability to fight infections, leading to bronchiectasis.
- Inhalation of harmful substances: Long-term exposure to inhaled irritants such as smoke, chemicals, or dust can also cause airway damage.
- Other diseases: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease can sometimes contribute to bronchiectasis.
Symptoms of Bronchiectasis
The symptoms of bronchiectasis typically include:













 +91-9818045855
+91-9818045855