Dr. Belal Bin Asaf
Thoracic (Chest) Surgeon
Director, Institute of Chest Surgery,
Chest Onco-Surgery & Lung Transplantation, Medanta Hospital

Dr. Belal Bin Asaf
Thoracic (Chest) Surgeon
Director, Institute of Chest Surgery,
Chest Onco-Surgery & Lung Transplantation, Medanta Hospital

Thymoma is a tumour that arises from the thymus gland, a small gland located in the upper chest just behind the breastbone (sternum). The thymus gland plays a key role in the development of the immune system during childhood. In adults, it usually shrinks but can sometimes develop abnormal cell growth, leading to formation of a tumour called thymoma.
Although many thymomas are slow growing, they must be taken seriously because they can invade nearby structures or, over time, become more aggressive.
The exact cause of thymoma is not fully understood, but it arises when certain cells of the thymus begin to grow uncontrollably. This is not something patients do or do not do; it is usually not linked to lifestyle factors.
The thymus helps teach the body’s immune cells (T-cells) to distinguish between “self” and “foreign” substances. Abnormal growth in the thymus can sometimes confuse the immune system, contributing to autoimmune disorders such as Myasthenia Gravis (MG)..
Many patients have no symptoms. Thymoma is often discovered incidentally during a chest X-ray or CT scan done for another reason.
When symptoms occur, they may include:
Early evaluation by a thoracic surgeon is crucial in such cases to ensure both the tumour and the autoimmune component are properly addressed.
A common myth is that a “small” or asymptomatic thymoma can be safely left alone. This is not true. Even small thymomas may:
Timely surgery offers the best chance of cure and prevents complications.
Imaging Studies
Blood Investigations
Routine blood investigations may be required to asses the patient’s fitness for undergoing treatment.
Apart from the routine investigations AChR-Antibody test may be ordered to look for myasthenia gravis
Other tests
Certain other tests may be required to rule out conditions that may be associated with Thymoma like:
Biopsy Considerations
Staging
Doctors often describe thymoma using:
Your surgeon will explain the stage in simple terms and how it affects treatment decisions.
Thymoma is categorized into different stages based on the extent of tumor spread. The Modified Masaoka-Koga staging system is commonly used to determine the appropriate treatment plan and prognosis. Here’s a detailed explanation of each stage:

Description: The tumor is completely encapsulated and confined within the thymus. It has not spread to surrounding tissues or organs.

Description: The tumor shows microscopic transcapsular invasion into the surrounding fatty tissue that is not appreciated grossly and is only visible under microscope.

Description: Description: The tumour exhibits macroscopic (grossly visible) invasion into the surrounding fatty tissue and may be touching the pleura but not invading through it.

Description: The thymoma has invaded neighbouring organs such as the pericardium (heart lining), lungs, or major blood vessels.

Description: The tumor has spread to the pleural or pericardial surfaces, leading to multiple tumor nodules in these areas.

Description: The thymoma has spread to distant lymph nodes or other organs via the bloodstream.
Surgery – The Cornerstone
For localised and resectable thymomas, complete surgical removal (thymectomy) is the standard and most effective treatment.
Multidisciplinary Care
At Medanta Hospitals, thymoma patients are treated by a team of thoracic surgeons, neurologists, oncologists, anaesthetists, and ICU specialists, ensuring comprehensive care tailored to each patient.
Surgical Approaches to Thymectomy
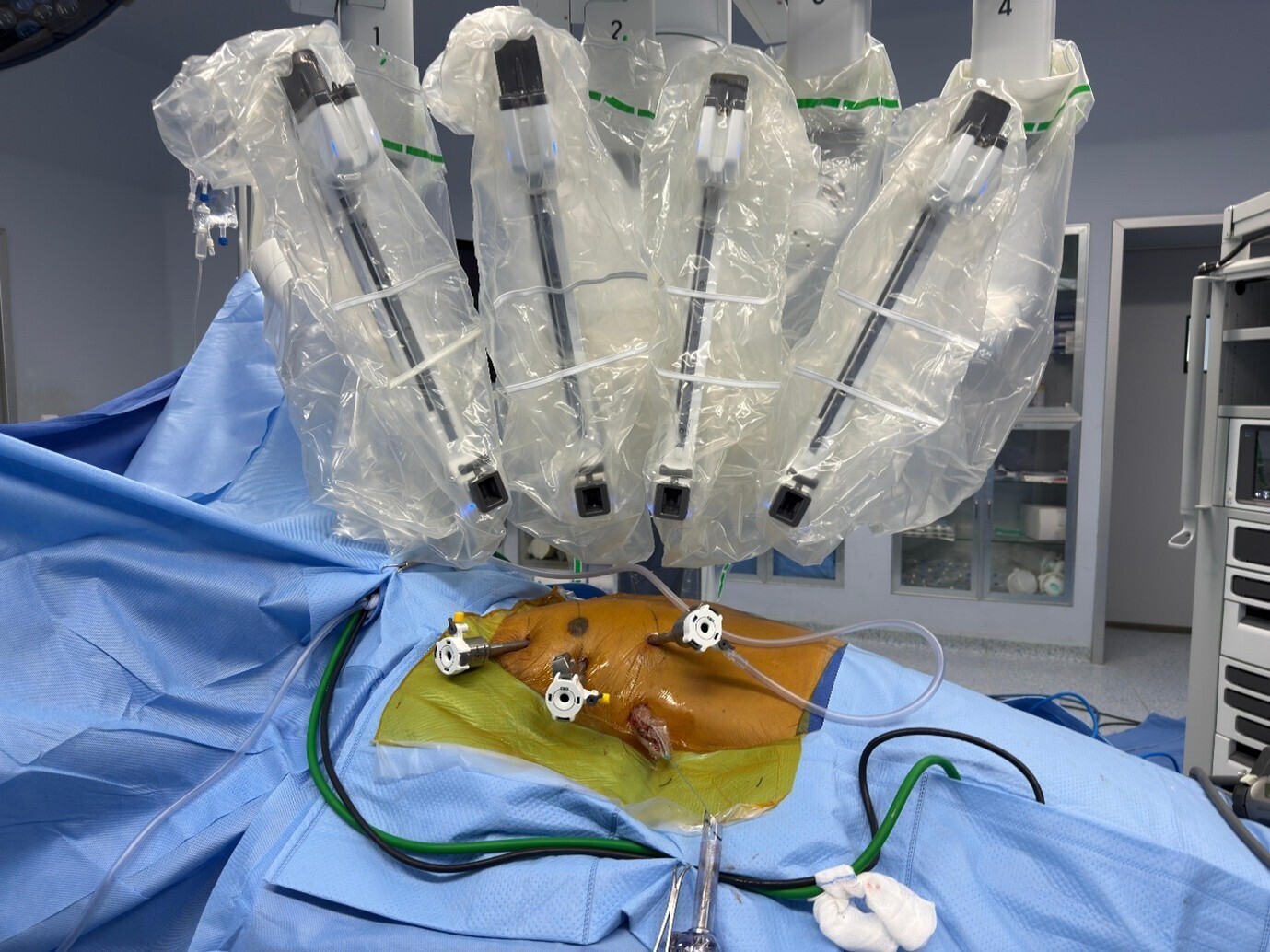
Dr Belal Bin Asaf is among the most experienced robotic thoracic surgeons in India and performed India’s first robotic subxiphoid thymectomy.
Advantages of the Subxiphoid Approach
Many patients can return home within 3–4 days of surgery.
Recovery & Long-Term Outcomes
Surgery is typically the best treatment option for Stage I thymomas. Complete surgical resection results in excellent long-term outcomes. Most tumours in this stage can be managed by minimally invasive chest surgery like Robotic Thymectomy or VATS /Thoracoscopic Thymectomy.
Prognosis: Patients diagnosed at this stage generally have a favorable prognosis with high long term survival rates.
urgery is still highly efficacious and the primary treatment. Complete surgery can still be achieved by Robotic surgery or Thoracoscopic surgery in many patients.
Prognosis:Prognosis remains good, with a high likelihood of successful treatment and long-term survival.
Surgical resection is the mainstay of treatment, often may be followed by radiotherapy to address any remaining cancer cells and prevent recurrence.
Prognosis: The prognosis is slightly less favourable than Stage I and IIA but still generally positive with appropriate treatment. Completeness of tumour removal plays a major role in the outcome, and hence, an experienced surgical team should address such cases. In experienced hands, a significant proportion of such patients can be managed by robotic thymectomy
Surgery is more complex and may involve removing parts of invaded organs. This is usually followed by radiotherapy and sometimes chemotherapy, especially if complete resection is not possible. Evaluation of such patients by a high-volume surgical team is very important as many of these cases can still be treated by surgery; however, the probability of robotic surgery is reduced. If the tumour is adherent to only the pericardium (lining of the heart) and/or a small portion of the adjacent lung, it can be managed by minimally invasive technique. Robotic surgery is better suited in such cases due to increased dexterity and precision.
Prognosis: Prognosis varies depending on the extent of invasion and the success of the surgical resection. Multimodal treatment improves outcomes. With complete removal of the tumour by experienced surgical team can give best outcomes in in some locally advanced cases.
Stage 4a Thymomas are treated by a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy. Many people think that surgery is not possible in cases of Thymoma that has spread to the pleura (lining of Lungs) of the pericardium (Lining of the heart). However, surgery is still very useful, where in the tumour is removed along with a complete removal of all nodules (achieved by total pleurectomy / pericardiectomy). In these cases some form of additional treatment in the form of adjuvant chemotherapy and radiation therapy is almost always required.
A form of chemotherapy which is given during surgery may also be used in selected patients. It is known as HITHOC. Hyperthermic Intrathoracic Chemotherapy (HITHOC) is an advanced treatment option for thymoma, especially in cases where the cancer has spread within the chest cavity. After surgical removal of the tumor, a heated chemotherapy solution is circulated within the chest cavity to eliminate any remaining cancer cells. The heat enhances the effectiveness of the chemotherapy, improving its ability to target and destroy cancer cells while minimizing side effects. HITHOC offers an innovative approach to reduce the risk of cancer recurrence and improve overall treatment outcomes. This innovative therapy is being done frequently by our team.
Prognosis: Prognosis is more guarded, and aggressive multimodal treatment is necessary to manage the disease. However relatively long survival has been reported by surgery along with other therapies.
In stage 4b the disease has spread beyond the confines of thymus gland through blood and lymph. Local therapy alone in the form of surgery will not be sufficient. Systemic chemotherapy is typically the primary treatment approach, often combined with radiotherapy. Surgery may be considered in select cases to alleviate symptoms or manage localized disease.
Prognosis: Stage IVB represents advanced disease and the prognosis is not as good as in early stages.
Modern anaesthesia and minimally invasive techniques have made thymectomy safe and well-tolerated in most patients.
No – in fact, complete removal prevents spread. Careful surgical handling avoids any risk of tumour seeding.
Yes – robotic systems are well-validated globally. Success depends on the surgeon’s expertise.
Delays can allow the tumour to invade nearby structures, making surgery more difficult and outcomes less favourable.
Still have questions about Aspergilloma and its treatment? Book a consultation with Dr. Belal Bin Asaf, one of India’s leading thoracic surgeons, for expert advice and personalized care.
Early and complete removal of thymoma by a specialist thoracic surgeon gives the best chance for cure and improved quality of life.
If you or your loved one has been diagnosed with thymoma or Myasthenia Gravis, or if a chest scan has revealed a mass near the thymus gland:
Receive a comprehensive evaluation and a personalised treatment plan based on the latest evidence and advanced minimally invasive techniques.
Facing a diagnosis of thymoma can be stressful, but timely information and expert care make all the difference.
With modern robotic surgery and a dedicated multidisciplinary team, the outlook for most thymoma patients today is very positive.
You are not alone on this journey – compassionate, expert help is available.
We are here for you! How can we help?

Director
Institute Of Chest Surgery, Chest
Onco-Surgery & Lung Transplantation