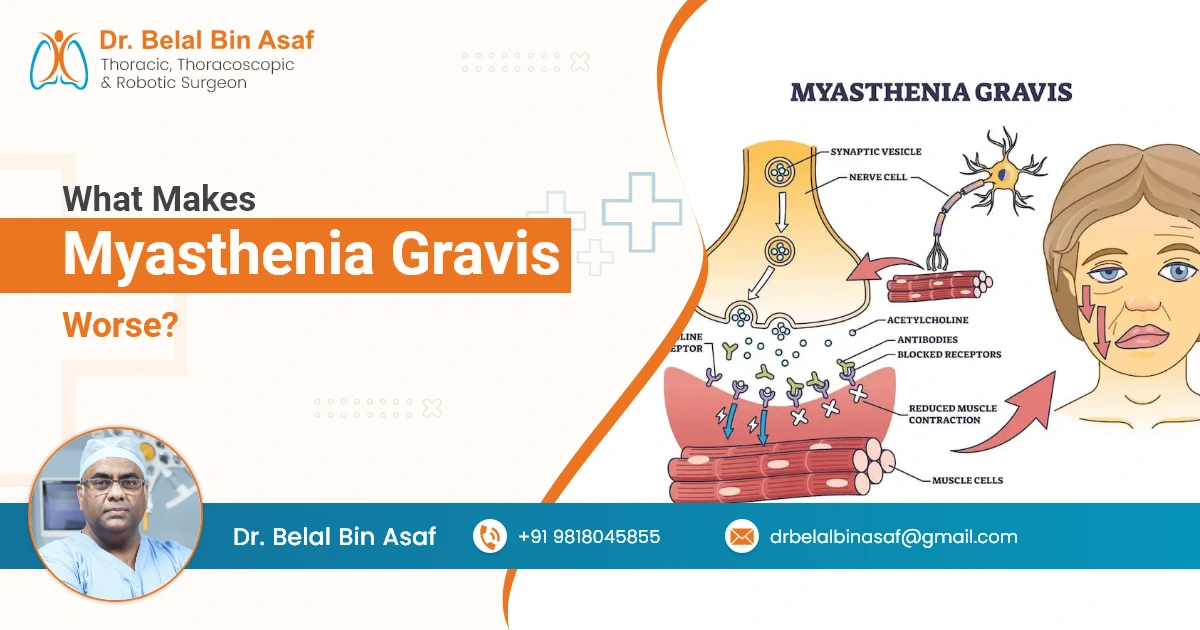
Myasthenia Gravis (MG) is a chronic autoimmune neuromuscular disorder that causes weakness in the skeletal muscles, which control voluntary movements. This condition occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the communication between nerves and muscles, particularly the acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction. These receptors are responsible for transmitting nerve signals to muscles, allowing them to contract. When these receptors are damaged or blocked, it leads to muscle weakness, which can affect essential functions such as speaking, swallowing, breathing, and general mobility.
While Myasthenia Gravis can vary from person to person, certain factors can exacerbate the condition. Understanding what worsens MG symptoms is crucial in managing the disease effectively. This blog explores various factors that can make Myasthenia Gravis worse, including infections, emotional and physical stress, environmental influences, sleep disturbances, diet, and hormonal changes.
Contents
- 1 Infections: A Major Trigger for Worsening Symptoms
- 2 Emotional and Physical Stress: A Hidden Culprit
- 3 Weather Conditions: The Impact of Extreme Temperatures
- 4 Sleep and Fatigue: The Vicious Cycle
- 5 Diet and Nutrition: Fueling the Body Properly
- 6 Hormonal Changes: The Role of Hormones in MG Progression
- 7 Conclusion
Infections: A Major Trigger for Worsening Symptoms
Infections are one of the most common triggers for worsening Myasthenia Gravis symptoms. Respiratory infections, such as the flu, pneumonia, or even the common cold, can exacerbate muscle weakness. When the body fights off an infection, the immune system becomes more active, and this can result in an increase in inflammation that negatively affects the neuromuscular junction.
People with MG are already at a higher risk for respiratory problems due to weakened respiratory muscles. An infection in the respiratory system can, therefore, worsen the symptoms, sometimes leading to a “myasthenic crisis,” where the symptoms become more severe, and respiratory failure may occur.














 +91-9818045855
+91-9818045855